Speech to Text with OpenVINO¶
This tutorial demonstrates speech-to-text recognition with OpenVINO.
For this tutorial, we use the quartznet 15x5 model. QuartzNet performs automatic speech recognition. Its design is based on the Jasper architecture, which is a convolutional model trained with Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) loss. The model is available from Open Model Zoo.
Imports¶
from pathlib import Path
import IPython.display as ipd
import librosa
import librosa.display
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import scipy
from openvino.runtime import Core
Settings¶
In this part, set up all variables used in the notebook.
model_folder = "model"
download_folder = "output"
data_folder = "data"
precision = "FP16"
model_name = "quartznet-15x5-en"
Download and Convert Public Model¶
If it is your first run, models will be downloaded and converted here.
It my take a few minutes. We use omz_downloader and
omz_converter, which are command-line tools from the
openvino-dev package.
Download Model¶
omz_downloader automatically creates a directory structure and
downloads the selected model. This step is skipped if the model is
already downloaded. The selected model comes from the public directory,
which means it must be converted into Intermediate Representation (IR).
# Check if model is already downloaded in download directory
path_to_model_weights = Path(f'{download_folder}/public/{model_name}/models')
downloaded_model_file = list(path_to_model_weights.glob('*.pth'))
if not path_to_model_weights.is_dir() or len(downloaded_model_file) == 0:
download_command = f"omz_downloader --name {model_name} --output_dir {download_folder} --precision {precision}"
! $download_command
################|| Downloading quartznet-15x5-en ||################
========== Downloading output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/ruamel.yaml-0.17.2-py3-none-any.whl
========== Downloading output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/nemo_toolkit-0.11.0-py3-none-any.whl
========== Downloading output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/QuartzNet15x5-En-Base.nemo
========== Unpacking output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/nemo_toolkit-0.11.0-py3-none-any.whl
========== Unpacking output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/QuartzNet15x5-En-Base.nemo
========== Unpacking output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/ruamel.yaml-0.17.2-py3-none-any.whl
========== Replacing text in output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/nemo/collections/asr/parts/dataset.py
========== Replacing text in output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/nemo/utils/helpers.py
========== Replacing text in output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/nemo/utils/env_var_parsing.py
========== Replacing text in output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/nemo/utils/neural_graph/graph_inputs.py
========== Replacing text in output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/nemo/utils/neural_graph/graph_outputs.py
========== Replacing text in output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/nemo/collections/asr/parts/__init__.py
========== Replacing text in output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/nemo/collections/asr/__init__.py
========== Replacing text in output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/nemo/collections/asr/__init__.py
========== Replacing text in output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/nemo/collections/asr/__init__.py
========== Replacing text in output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/nemo/constants.py
========== Replacing text in output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/nemo/collections/asr/jasper.py
Convert Model¶
omz_converter is needed to convert pre-trained PyTorch model to
ONNX model format, which is further converted to OpenVINO IR format.
Both stages of conversion are handled by calling omz_converter.
# Check if model is already converted in model directory
path_to_converted_weights = Path(f'{model_folder}/public/{model_name}/{precision}/{model_name}.bin')
if not path_to_converted_weights.is_file():
convert_command = f"omz_converter --name {model_name} --precisions {precision} --download_dir {download_folder} --output_dir {model_folder}"
! $convert_command
========== Converting quartznet-15x5-en to ONNX
Conversion to ONNX command: /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.8.12/x64/bin/python -- /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.8.12/x64/lib/python3.8/site-packages/openvino/model_zoo/internal_scripts/pytorch_to_onnx.py --model-path=/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.8.12/x64/lib/python3.8/site-packages/openvino/model_zoo/models/public/quartznet-15x5-en --model-path=output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models --model-name=QuartzNet --import-module=model --input-shape=1,64,128 --output-file=model/public/quartznet-15x5-en/quartznet.onnx '--model-param=model_config=r"output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/.nemo_tmp/module.yaml"' '--model-param=encoder_weights=r"output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/.nemo_tmp/JasperEncoder.pt"' '--model-param=decoder_weights=r"output/public/quartznet-15x5-en/models/.nemo_tmp/JasperDecoderForCTC.pt"' --input-names=audio_signal --output-names=output
[NeMo W 2022-05-31 16:14:49 jasper:148] Turned off 170 masked convolutions
ONNX check passed successfully.
========== Converting quartznet-15x5-en to IR (FP16)
Conversion command: /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.8.12/x64/bin/python -- /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.8.12/x64/bin/mo --framework=onnx --data_type=FP16 --output_dir=model/public/quartznet-15x5-en/FP16 --model_name=quartznet-15x5-en --input=audio_signal --output=output --input_model=model/public/quartznet-15x5-en/quartznet.onnx '--layout=audio_signal(NCH)' '--input_shape=[1, 64, 128]'
Model Optimizer arguments:
Common parameters:
- Path to the Input Model: /home/runner/work/openvino_notebooks/openvino_notebooks/notebooks/211-speech-to-text/model/public/quartznet-15x5-en/quartznet.onnx
- Path for generated IR: /home/runner/work/openvino_notebooks/openvino_notebooks/notebooks/211-speech-to-text/model/public/quartznet-15x5-en/FP16
- IR output name: quartznet-15x5-en
- Log level: ERROR
- Batch: Not specified, inherited from the model
- Input layers: audio_signal
- Output layers: output
- Input shapes: [1, 64, 128]
- Source layout: Not specified
- Target layout: Not specified
- Layout: audio_signal(NCH)
- Mean values: Not specified
- Scale values: Not specified
- Scale factor: Not specified
- Precision of IR: FP16
- Enable fusing: True
- User transformations: Not specified
- Reverse input channels: False
- Enable IR generation for fixed input shape: False
- Use the transformations config file: None
Advanced parameters:
- Force the usage of legacy Frontend of Model Optimizer for model conversion into IR: False
- Force the usage of new Frontend of Model Optimizer for model conversion into IR: False
OpenVINO runtime found in: /opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.8.12/x64/lib/python3.8/site-packages/openvino
OpenVINO runtime version: 2022.1.0-7019-cdb9bec7210-releases/2022/1
Model Optimizer version: 2022.1.0-7019-cdb9bec7210-releases/2022/1
[ SUCCESS ] Generated IR version 11 model.
[ SUCCESS ] XML file: /home/runner/work/openvino_notebooks/openvino_notebooks/notebooks/211-speech-to-text/model/public/quartznet-15x5-en/FP16/quartznet-15x5-en.xml
[ SUCCESS ] BIN file: /home/runner/work/openvino_notebooks/openvino_notebooks/notebooks/211-speech-to-text/model/public/quartznet-15x5-en/FP16/quartznet-15x5-en.bin
[ SUCCESS ] Total execution time: 1.31 seconds.
[ SUCCESS ] Memory consumed: 216 MB.
It's been a while, check for a new version of Intel(R) Distribution of OpenVINO(TM) toolkit here https://software.intel.com/content/www/us/en/develop/tools/openvino-toolkit/download.html?cid=other&source=prod&campid=ww_2022_bu_IOTG_OpenVINO-2022-1&content=upg_all&medium=organic or on the GitHub*
[ INFO ] The model was converted to IR v11, the latest model format that corresponds to the source DL framework input/output format. While IR v11 is backwards compatible with OpenVINO Inference Engine API v1.0, please use API v2.0 (as of 2022.1) to take advantage of the latest improvements in IR v11.
Find more information about API v2.0 and IR v11 at https://docs.openvino.ai
Audio Processing¶
Now that the model is converted, load an audio file.
Defining constants¶
First, locate an audio file and define the alphabet used by the model.
In this tutorial, we will use the Latin alphabet beginning with a space
symbol and ending with a blank symbol, in our case it will be ~, but
that could be any other character.
audio_file_name = "edge_to_cloud.ogg"
alphabet = " abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'~"
Availble Audio Formats¶
There are multiple audio formats that can be used with the model.
List of supported audio formats:
AIFF, AU, AVR, CAF, FLAC, HTK, SVX, MAT4, MAT5, MPC2K, OGG, PAF, PVF, RAW, RF64, SD2, SDS, IRCAM, VOC, W64, WAV, NIST, WAVEX, WVE, XI
Load Audio File¶
After checking file extension, you have to load the file. As an
additional parameter, you have to pass sr which stands for
sampling rate. Model is supporting files with sampling rate of
16 kHz.
audio, sampling_rate = librosa.load(path=f'{data_folder}/{audio_file_name}', sr=16000)
You can play your audio file.
ipd.Audio(audio, rate=sampling_rate)
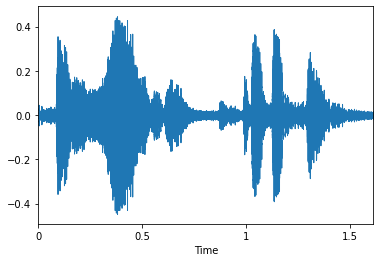
Visualise Audio File¶
You can visualize how your audio file presents on a wave plot and spectrogram.
plt.figure()
librosa.display.waveplot(y=audio, sr=sampling_rate, max_points=50000.0, x_axis='time', offset=0.0, max_sr=1000);
plt.show()
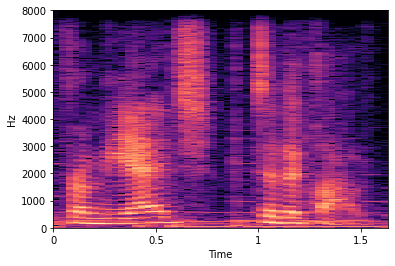
specto_audio = librosa.stft(audio)
specto_audio = librosa.amplitude_to_db(np.abs(specto_audio), ref=np.max)
print(specto_audio.shape)
librosa.display.specshow(specto_audio, sr=sampling_rate, x_axis='time', y_axis='hz');
(1025, 51)
Change Type of Data¶
The file loaded in previous step may contain data in float type with
a range of values between -1 and 1. To generate viable input, we have to
multiply each value by the max value of int16 and convert it to
int16 type.
if max(np.abs(audio)) <= 1:
audio = (audio * (2**15 - 1))
audio = audio.astype(np.int16)
Convert Audio to Mel Spectrum¶
Next, we need to convert our pre-pre-processed audio to Mel Spectrum. To learn more about why we do this, see this article.
def audio_to_mel(audio, sampling_rate):
assert sampling_rate == 16000, "Only 16 KHz audio supported"
preemph = 0.97
preemphased = np.concatenate([audio[:1], audio[1:] - preemph * audio[:-1].astype(np.float32)])
# Calculate window length
win_length = round(sampling_rate * 0.02)
# Based on previously calculated window length run short-time Fourier transform
spec = np.abs(librosa.core.spectrum.stft(preemphased, n_fft=512, hop_length=round(sampling_rate * 0.01),
win_length=win_length, center=True, window=scipy.signal.windows.hann(win_length), pad_mode='reflect'))
# Create mel filter-bank, produce transformation matrix to project current values onto Mel-frequency bins
mel_basis = librosa.filters.mel(sampling_rate, 512, n_mels=64, fmin=0.0, fmax=8000.0, htk=False)
return mel_basis, spec
def mel_to_input(mel_basis, spec, padding=16):
# Convert to logarithmic scale
log_melspectrum = np.log(np.dot(mel_basis, np.power(spec, 2)) + 2 ** -24)
# Normalize output
normalized = (log_melspectrum - log_melspectrum.mean(1)[:, None]) / (log_melspectrum.std(1)[:, None] + 1e-5)
# Calculate padding
remainder = normalized.shape[1] % padding
if remainder != 0:
return np.pad(normalized, ((0, 0), (0, padding - remainder)))[None]
return normalized[None]
Run Conversion from Audio to Mel Format¶
In this step, you want to convert a current audio file into Mel scale.
mel_basis, spec = audio_to_mel(audio=audio.flatten(), sampling_rate=sampling_rate)
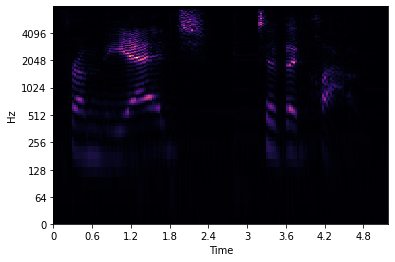
Visualise Mel Spectogram¶
If you want to know more about Mel spectrogram follow this link. The first image visualizes Mel frequency spectrogram, the second one presents filter bank for converting Hz to Mels.
librosa.display.specshow(data=spec, sr=sampling_rate, x_axis='time', y_axis='log');
plt.show();
librosa.display.specshow(data=mel_basis, sr=sampling_rate, x_axis='linear');
plt.ylabel('Mel filter');
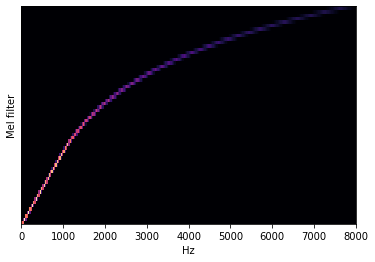
Adjust Mel scale to Input¶
Before reading the network, check that the input is ready.
audio = mel_to_input(mel_basis=mel_basis, spec=spec)
Load Model¶
Now, we can read and load network.
ie = Core()
You may choose to run the network on multiple devices. By default, it will load the model on the CPU (you can choose manually CPU, GPU, MYRIAD, etc.) or let the engine choose the best available device (AUTO).
To list all available devices that you can use, run line
print(ie.available_devices).
print(ie.available_devices)
['CPU']
To change device used for your network change value of variable
device_name to one of the values listed by print in the cell above.
model = ie.read_model(
model=f"{model_folder}/public/{model_name}/{precision}/{model_name}.xml"
)
model_input_layer = model.input(0)
shape = model_input_layer.partial_shape
shape[2] = -1
model.reshape({model_input_layer: shape})
compiled_model = ie.compile_model(model=model, device_name="CPU")
Do Inference¶
Everything is set up. Now the only thing remaining is passing input to the previously loaded network and running inference.
output_layer_ir = compiled_model.output(0)
character_probabilities = compiled_model([audio])[output_layer_ir]
Read Output¶
After inference, you need to reach out the output. The default output
format for quartznet 15x5 are per-frame probabilities (after
LogSoftmax) for every symbol in the alphabet, name - output, shape -
1x64x29, output data format is BxNxC, where:
B - batch size
N - number of audio frames
C - alphabet size, including the Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) blank symbol
You need to make it in a more human-readable format. To do this you, use a symbol with the highest probability. When you hold a list of indexes that are predicted to have the highest probability, due to limitations given by Connectionist Temporal Classification Decoding you will remove concurrent symbols and then remove all the blanks.
The last step is getting symbols from corresponding indexes in charlist.
# Remove unnececery dimension
character_probabilities = np.squeeze(character_probabilities)
# Run argmax to pick most possible symbols
character_probabilities = np.argmax(character_probabilities, axis=1)
Implementation of Decoding¶
To decode previously explained output we need Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) decode function. This solution will remove consecutive letters from the output.
def ctc_greedy_decode(predictions):
previous_letter_id = blank_id = len(alphabet) - 1
transcription = list()
for letter_index in predictions:
if previous_letter_id != letter_index != blank_id:
transcription.append(alphabet[letter_index])
previous_letter_id = letter_index
return ''.join(transcription)
Run Decoding and Print Output¶
transcription = ctc_greedy_decode(character_probabilities)
print(transcription)
from the edge to the cloud