PaddleOCR with OpenVINO¶
This demo shows how to run PPOCR model on OpenVINO natively. Instead of exporting the PaddlePaddle model to ONNX and then convert to the Intermediate Representation (IR) format through OpenVINO Model Optimizer, we can now read directly from the PaddlePaddle Model without any conversions. PaddleOCR is an ultra-light OCR model trained with PaddlePaddle deep learning framework, that aims to create multilingual and practical OCR tools.
The paddleOCR pre-trained model used in the demo refer to the “Chinese and English ultra-lightweight PP-OCR model (9.4M)”. More open-sourced pre-trained models could be downloaded at PaddleOCR Github or PaddleOCR Gitee. Working pipeline of the paddleOCR is as follows:
Note: To use this notebook with a webcam, you need to run the notebook on a computer with a webcam. If you run the notebook on a server, the webcam will not work. You can still do inference on a video.
Imports¶
import sys
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
import paddle
import math
import time
import collections
from PIL import Image
from pathlib import Path
import tarfile
import urllib.request
from openvino.runtime import Core
from IPython import display
import copy
sys.path.append("../utils")
import notebook_utils as utils
import pre_post_processing as processing
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.8.12/x64/lib/python3.8/site-packages/paddle/vision/transforms/functional_pil.py:36: DeprecationWarning: NEAREST is deprecated and will be removed in Pillow 10 (2023-07-01). Use Resampling.NEAREST or Dither.NONE instead.
'nearest': Image.NEAREST,
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.8.12/x64/lib/python3.8/site-packages/paddle/vision/transforms/functional_pil.py:37: DeprecationWarning: BILINEAR is deprecated and will be removed in Pillow 10 (2023-07-01). Use Resampling.BILINEAR instead.
'bilinear': Image.BILINEAR,
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.8.12/x64/lib/python3.8/site-packages/paddle/vision/transforms/functional_pil.py:38: DeprecationWarning: BICUBIC is deprecated and will be removed in Pillow 10 (2023-07-01). Use Resampling.BICUBIC instead.
'bicubic': Image.BICUBIC,
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.8.12/x64/lib/python3.8/site-packages/paddle/vision/transforms/functional_pil.py:39: DeprecationWarning: BOX is deprecated and will be removed in Pillow 10 (2023-07-01). Use Resampling.BOX instead.
'box': Image.BOX,
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.8.12/x64/lib/python3.8/site-packages/paddle/vision/transforms/functional_pil.py:40: DeprecationWarning: LANCZOS is deprecated and will be removed in Pillow 10 (2023-07-01). Use Resampling.LANCZOS instead.
'lanczos': Image.LANCZOS,
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.8.12/x64/lib/python3.8/site-packages/paddle/vision/transforms/functional_pil.py:41: DeprecationWarning: HAMMING is deprecated and will be removed in Pillow 10 (2023-07-01). Use Resampling.HAMMING instead.
'hamming': Image.HAMMING
Models for PaddleOCR¶
PaddleOCR includes two parts of deep learning models, text detection and text recognition. Pre-trained models used in the demo are downloaded and stored in the “model” folder. Other pre-trained models for PaddleOCR could be download at PaddleOCR Github or PaddleOCR Gitee.
Only a few lines of code are required to run the model. First, we
initialize the runtime for inference. Then we read the network
architecture and model weights from the .pdmodel and .pdiparams
files to load onto the CPU.
# Define the function to download text detection and recognition models from PaddleOCR resources
def run_model_download(model_url, model_file_path):
"""
Download pre-trained models from PaddleOCR resources
Parameters:
model_url: url link to pre-trained models
model_file_path: file path to store the downloaded model
"""
model_name = model_url.split("/")[-1]
if model_file_path.is_file():
print("Model already exists")
else:
# Download the model from the server, and untar it.
print("Downloading the pre-trained model... May take a while...")
# create a directory
os.makedirs("model", exist_ok=True)
urllib.request.urlretrieve(model_url, f"model/{model_name} ")
print("Model Downloaded")
file = tarfile.open(f"model/{model_name} ")
res = file.extractall("model")
file.close()
if not res:
print(f"Model Extracted to {model_file_path}.")
else:
print("Error Extracting the model. Please check the network.")
Download the Model for Text Detection¶
# Directory where model will be downloaded
det_model_url = "https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_det_infer.tar"
det_model_file_path = Path("model/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_det_infer/inference.pdmodel")
run_model_download(det_model_url, det_model_file_path)
Downloading the pre-trained model... May take a while...
Model Downloaded
Model Extracted to model/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_det_infer/inference.pdmodel.
Load the Model for Text Detection¶
# initialize inference engine for text detection
core = Core()
det_model = core.read_model(model=det_model_file_path)
det_compiled_model = core.compile_model(model=det_model, device_name="CPU")
# get input and output nodes for text detection
det_input_layer = det_compiled_model.input(0)
det_output_layer = det_compiled_model.output(0)
Download the Model for Text Recognition¶
rec_model_url = "https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/dygraph_v2.0/ch/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_rec_infer.tar"
rec_model_file_path = Path("model/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_rec_infer/inference.pdmodel")
run_model_download(rec_model_url, rec_model_file_path)
Downloading the pre-trained model... May take a while...
Model Downloaded
Model Extracted to model/ch_ppocr_mobile_v2.0_rec_infer/inference.pdmodel.
Load the Model for Text Recognition with Dynamic Shape¶
Input to text recognition model refers to detected bounding boxes with different image sizes, i.e, dynamic input shapes. Hence:
Input dimension with dynamic input shapes needs to be specified before loading text recognition model
Dynamic shape is specified by assigning -1 to the input dimension or by setting the upper bound of the input dimension using, for example, Dimension(1, 512)
# read the model and corresponding weights from file
rec_model = core.read_model(model=rec_model_file_path)
# assign dynamic shapes to every input layer on the last dimension
for input_layer in rec_model.inputs:
input_shape = input_layer.partial_shape
input_shape[3] = -1
rec_model.reshape({input_layer: input_shape})
rec_compiled_model = core.compile_model(model=rec_model, device_name="CPU")
# get input and output nodes
rec_input_layer = rec_compiled_model.input(0)
rec_output_layer = rec_compiled_model.output(0)
Preprocessing image functions for text detection and recognition¶
Define preprosessing functions for text detection and recognition: 1. Preprocessing for text detection: resize and normalize input images 2. Preprocessing for text recognition: resize and normalize detected box images to the same size (e.g. size (3, 32, 320) for images with Chinese text) for easy batching in inference
# Preprocess for text detection
def image_preprocess(input_image, size):
"""
Preprocess input image for text detection
Parameters:
input_image: input image
size: value for the image to be resized for text detection model
"""
img = cv2.resize(input_image, (size, size))
img = np.transpose(img, [2, 0, 1]) / 255
img = np.expand_dims(img, 0)
# NormalizeImage: {mean: [0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std: [0.229, 0.224, 0.225], is_scale: True}
img_mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]).reshape((3, 1, 1))
img_std = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]).reshape((3, 1, 1))
img -= img_mean
img /= img_std
return img.astype(np.float32)
# Preprocess for text recognition
def resize_norm_img(img, max_wh_ratio):
"""
Resize input image for text recognition
Parameters:
img: bounding box image from text detection
max_wh_ratio: value for the resizing for text recognition model
"""
rec_image_shape = [3, 32, 320]
imgC, imgH, imgW = rec_image_shape
assert imgC == img.shape[2]
character_type = "ch"
if character_type == "ch":
imgW = int((32 * max_wh_ratio))
h, w = img.shape[:2]
ratio = w / float(h)
if math.ceil(imgH * ratio) > imgW:
resized_w = imgW
else:
resized_w = int(math.ceil(imgH * ratio))
resized_image = cv2.resize(img, (resized_w, imgH))
resized_image = resized_image.astype('float32')
resized_image = resized_image.transpose((2, 0, 1)) / 255
resized_image -= 0.5
resized_image /= 0.5
padding_im = np.zeros((imgC, imgH, imgW), dtype=np.float32)
padding_im[:, :, 0:resized_w] = resized_image
return padding_im
def batch_text_box(dt_boxes, frame):
"""
Batch the detected bounding boxes for text recognition
Parameters:
dt_boxes: detected bounding boxes from text detection
frame: original input frame
"""
ori_im = frame.copy()
img_crop_list = []
for bno in range(len(dt_boxes)):
tmp_box = copy.deepcopy(dt_boxes[bno])
img_crop = processing.get_rotate_crop_image(ori_im, tmp_box)
img_crop_list.append(img_crop)
img_num = len(img_crop_list)
# Calculate the aspect ratio of all text bars
width_list = []
for img in img_crop_list:
width_list.append(img.shape[1] / float(img.shape[0]))
# Sorting can speed up the recognition process
indices = np.argsort(np.array(width_list))
rec_res = [['', 0.0]] * img_num
batch_num = 6
# For each detected text box batch, run inference for text recognition
for beg_img_no in range(0, img_num, batch_num):
end_img_no = min(img_num, beg_img_no + batch_num)
norm_img_batch = []
max_wh_ratio = 0
for ino in range(beg_img_no, end_img_no):
h, w = img_crop_list[indices[ino]].shape[0:2]
wh_ratio = w * 1.0 / h
max_wh_ratio = max(max_wh_ratio, wh_ratio)
for ino in range(beg_img_no, end_img_no):
norm_img = resize_norm_img(img_crop_list[indices[ino]], max_wh_ratio)
norm_img = norm_img[np.newaxis, :]
norm_img_batch.append(norm_img)
norm_img_batch = np.concatenate(norm_img_batch)
norm_img_batch = norm_img_batch.copy()
return norm_img_batch, rec_res, indices, beg_img_no
Postprocessing image for text detection¶
def post_processing_detection(frame, det_results):
"""
Postprocess the results from text detection into bounding boxes
Parameters:
frame: input image
det_results: inference results from text detection model
"""
ori_im = frame.copy()
data = {'image': frame}
data_resize = processing.DetResizeForTest(data)
data_list = []
keep_keys = ['image', 'shape']
for key in keep_keys:
data_list.append(data_resize[key])
img, shape_list = data_list
shape_list = np.expand_dims(shape_list, axis=0)
pred = det_results[0]
if isinstance(pred, paddle.Tensor):
pred = pred.numpy()
segmentation = pred > 0.3
boxes_batch = []
for batch_index in range(pred.shape[0]):
src_h, src_w, ratio_h, ratio_w = shape_list[batch_index]
mask = segmentation[batch_index]
boxes, scores = processing.boxes_from_bitmap(pred[batch_index], mask, src_w, src_h)
boxes_batch.append({'points': boxes})
post_result = boxes_batch
dt_boxes = post_result[0]['points']
dt_boxes = processing.filter_tag_det_res(dt_boxes, ori_im.shape)
return dt_boxes
Main processing function for PaddleOCR¶
Run paddleOCR function in different operations, either a webcam or a video file. See the list of procedures below:
Create a video player to play with target fps (
utils.VideoPlayer).Prepare a set of frames for text detection and recognition.
Run AI inference for both text detection and recognition.
Visualize the results.
def run_paddle_ocr(source=0, flip=False, use_popup=False, skip_first_frames=0):
"""
Main function to run the paddleOCR inference:
1. Create a video player to play with target fps (utils.VideoPlayer).
2. Prepare a set of frames for text detection and recognition.
3. Run AI inference for both text detection and recognition.
4. Visualize the results.
Parameters:
source: the webcam number to feed the video stream with primary webcam set to "0", or the video path.
flip: to be used by VideoPlayer function for flipping capture image
use_popup: False for showing encoded frames over this notebook, True for creating a popup window.
skip_first_frames: Number of frames to skip at the beginning of the video.
"""
# create video player to play with target fps
player = None
try:
player = utils.VideoPlayer(source=source, flip=flip, fps=30, skip_first_frames=skip_first_frames)
# Start video capturing
player.start()
if use_popup:
title = "Press ESC to Exit"
cv2.namedWindow(winname=title, flags=cv2.WINDOW_GUI_NORMAL | cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)
processing_times = collections.deque()
while True:
# grab the frame
frame = player.next()
if frame is None:
print("Source ended")
break
# if frame larger than full HD, reduce size to improve the performance
scale = 1280 / max(frame.shape)
if scale < 1:
frame = cv2.resize(src=frame, dsize=None, fx=scale, fy=scale,
interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
# preprocess image for text detection
test_image = image_preprocess(frame,640)
# measure processing time for text detection
start_time = time.time()
# perform the inference step
det_results = det_compiled_model([test_image])[det_output_layer]
stop_time = time.time()
# Postprocessing for Paddle Detection
dt_boxes = post_processing_detection(frame, det_results)
processing_times.append(stop_time - start_time)
# use processing times from last 200 frames
if len(processing_times) > 200:
processing_times.popleft()
processing_time_det = np.mean(processing_times) * 1000
# Preprocess detection results for recognition
dt_boxes = processing.sorted_boxes(dt_boxes)
if dt_boxes:
# Recognition starts from here
norm_img_batch, rec_res, indices, beg_img_no = batch_text_box(dt_boxes, frame)
# Run inference for text recognition
rec_results = rec_compiled_model([norm_img_batch])[rec_output_layer]
# Postprocessing recognition results
postprocess_op = processing.build_post_process(processing.postprocess_params)
rec_result = postprocess_op(rec_results)
for rno in range(len(rec_result)):
rec_res[indices[beg_img_no + rno]] = rec_result[rno]
# Text recognition results, rec_res, include two parts:
# txts are the recognized text results, scores are the recognition confidence level
if rec_res:
image = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
boxes = dt_boxes
txts = [rec_res[i][0] for i in range(len(rec_res))]
scores = [rec_res[i][1] for i in range(len(rec_res))]
# draw text recognition results beside the image
draw_img = processing.draw_ocr_box_txt(
image,
boxes,
txts,
scores,
drop_score=0.5)
else:
draw_img = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# Visualize PaddleOCR results
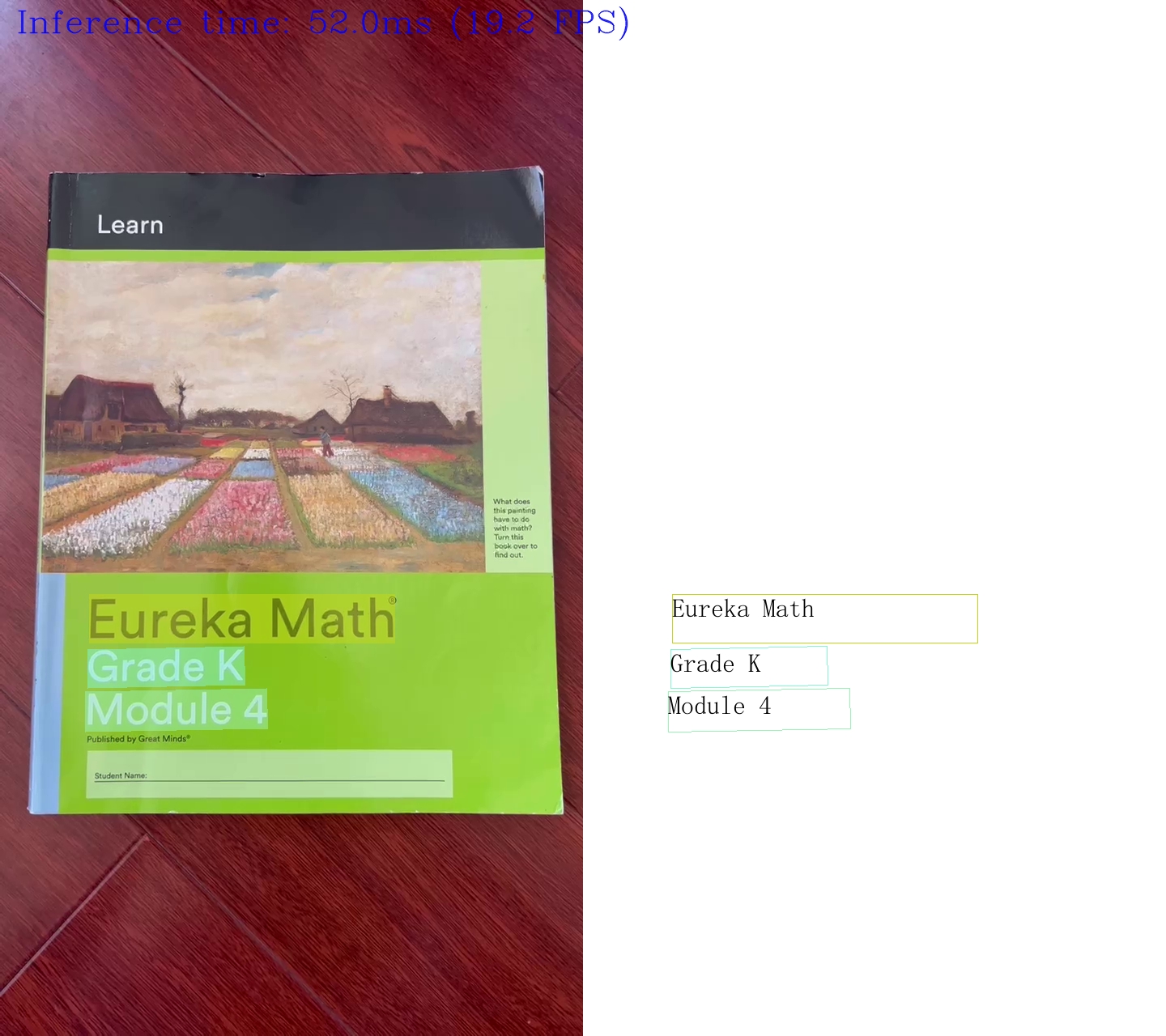
f_height, f_width = draw_img.shape[:2]
fps = 1000 / processing_time_det
cv2.putText(img=draw_img, text=f"Inference time: {processing_time_det:.1f}ms ({fps:.1f} FPS)",
org=(20, 40),fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, fontScale=f_height / 1000,
color=(0, 0, 255), thickness=1, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
# use this workaround if there is flickering
if use_popup:
draw_img = cv2.cvtColor(draw_img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
cv2.imshow(winname=title, mat=draw_img)
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
# escape = 27
if key == 27:
break
else:
# encode numpy array to jpg
draw_img = cv2.cvtColor(draw_img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
_, encoded_img = cv2.imencode(ext=".jpg", img=draw_img,
params=[cv2.IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY, 100])
# create IPython image
i = display.Image(data=encoded_img)
# display the image in this notebook
display.clear_output(wait=True)
display.display(i)
# ctrl-c
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Interrupted")
# any different error
except RuntimeError as e:
print(e)
finally:
if player is not None:
# stop capturing
player.stop()
if use_popup:
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Run Live PaddleOCR with OpenVINO¶
Run using a webcam as the video input. By default, the primary webcam is
set with source=0. If you have multiple webcams, each one will be
assigned a consecutive number starting at 0. Set flip=True when
using a front-facing camera. Some web browsers, especially Mozilla
Firefox, may cause flickering. If you experience flickering, set
use_popup=True. Note popup mode may not work if you run this
notebook on a remote computer.
run_paddle_ocr(source=0, flip=False, use_popup=False)
Cannot open camera 0
If you don’t have a webcam, you can still run this demo with a video file. Any format supported by OpenCV will work.
# Test OCR results on video file
video_file = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yoyowz/classification/master/images/test.mp4"
run_paddle_ocr(source=video_file, flip=False, use_popup=False, skip_first_frames=0)
Source ended