Transition to OpenVINO™ API 2.0¶
Introduction¶
Versions of OpenVINO™ prior to 2022.1 required changes in the application logic when migrating an app from other frameworks, like TensorFlow, ONNX Runtime, PyTorch, PaddlePaddle, etc. The changes were required because:
Model Optimizer changed input precisions for some inputs. For example, neural language processing models with
I64inputs were changed to includeI32ones.Model Optimizer changed layouts for TensorFlow models (see the Layouts in OpenVINO). It lead to unusual requirement of using the input data with a different layout than that of the framework:
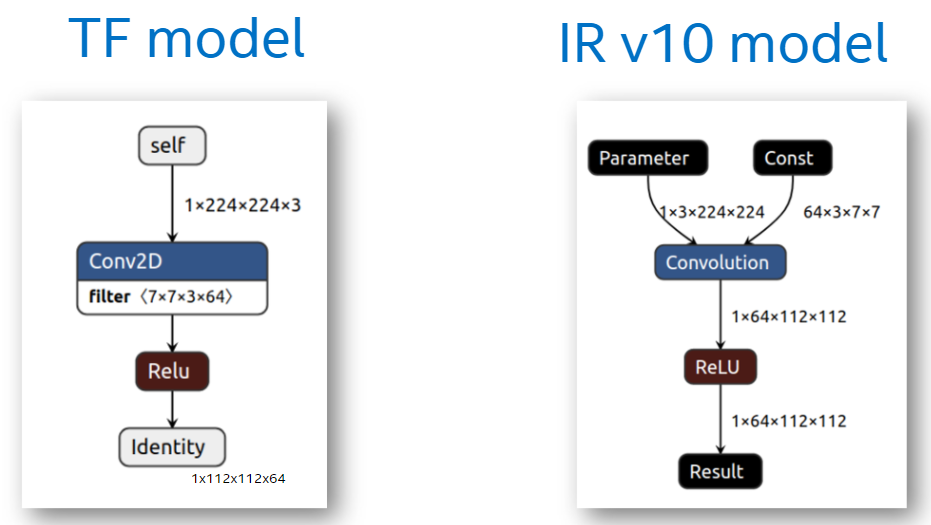
Inference Engine API (
InferenceEngine::CNNNetwork) applied some conversion rules for input and output precisions due to limitations in device plugins.Users needed to specify input shapes during model conversions in Model Optimizer, and work with static shapes in the application.
The new OpenVINO™ introduces API 2.0 (also called OpenVINO API v2) to align the logic of working with models as it is done in their origin frameworks - no layout and precision changes, operating with tensor names and indices to address inputs and outputs. OpenVINO Runtime has combined Inference Engine API used for inference and nGraph API targeted to work with models and operations. API 2.0 has a common structure, naming convention styles, namespaces, and removes duplicated structures. For more details, see the Changes to Inference Pipeline in OpenVINO API v2.
Note
Your existing applications will continue to work with OpenVINO Runtime 2022.1, as normal. Although, migration to API 2.0 is strongly recommended. This will allow you to use additional features, like Preprocessing and Dynamic shapes support.
Introducing IR v11¶
To support these features, OpenVINO has introduced IR v11, which is now the default version for Model Optimizer. The model represented in IR v11 fully matches the original model in the original framework format in terms of inputs, and outputs. It is also not required to specify input shapes during conversion, which results in IR v11 containing -1 to denote undefined dimensions. For more details on how to fully utilize this feature, see the Working with dynamic shapes guide. For information on how to reshape to static shapes in the application, see the Changing input shapes.
IR v11 is fully compatible with old applications written with the Inference Engine API used by older versions of OpenVINO. This backward compatibility is allowed thanks to additional runtime information included in IR v11. This means that if the IR v11 is read by an application based on Inference Engine, it is internally converted to IR v10.
IR v11 is supported by all OpenVINO Development tools including Post-Training Optimization tool, Benchmark app, etc.
IR v10 Compatibility¶
API 2.0 also supports backward compatibility for models in IR v10. If you have IR v10 files, they can also be fed to OpenVINO Runtime (For more details, see the migration steps).
Some OpenVINO Development Tools also support both IR v10 and IR v11 as an input:
Accuracy checker uses API 2.0 for model accuracy measurement by default. It also supports switching to the old API by using the
--use_new_api Falsecommand line parameter. Both launchers accept IR v10 and v11, but in some cases configuration files should be updated. For more details, see the Accuracy Checker documentation.Compile tool compiles the model to be used in API 2.0 by default. To use the resulting compiled blob under the Inference Engine API, the additional
ov_api_1_0option should be passed.
Not all tools under the OpenVINO umbrella continue to support IR v10 and will require the latest version of Model Optimizer to generate IR v11 files. They are: Post-Training Optimization Tool and Deep Learning Workbench.
Note
If you need to quantize your IR v10 models to run with OpenVINO 2022.1, it is recommended to download, and use Post-Training Optimization tool from the OpenVINO 2021.4 release.
Differences between Inference Engine and OpenVINO Runtime 2022.1¶
Inference Engine and nGraph APIs have not become deprecated with the introduction of the new API, and they can still be used in applications. However, it is highly recommended to migrate to API 2.0, as it offers more features (further extended in future releases), such as:
Working with dynamic shapes increases performance when working with compatible models, such as NLP (Neural Language Processing) and super-resolution models.
Preprocessing of the model adds preprocessing operations to inference models, and fully occupies the accelerator, freeing CPU resources.
The API differences between Inference Engine, and API 2.0, can be defined by two types of behaviors:
Old behavior of OpenVINO assumes that:
Model Optimizer can change input element types, order of dimensions (layouts) for the model from the original framework.
Inference Engine can override input and output element types.
Inference Engine API uses operation names to address inputs and outputs (e.g. InferenceEngine::InferRequest::GetBlob).
Inference Engine API does not support compiling of models with dynamic input shapes.
New behavior assumes full model alignment with the framework and is implemented in OpenVINO 2022.1:
Model Optimizer preserves input element types, order of dimensions (layouts), and stores tensor names from the original models.
OpenVINO Runtime 2022.1 reads models in any format (IR v10, IR v11, ONNX, PaddlePaddle, etc.).
API 2.0 uses tensor names for addressing, which is the standard approach among the compatible model frameworks.
API 2.0 can also address input and output tensors by the index. Some model formats like ONNX are sensitive to the input, and output order, which is preserved by OpenVINO 2022.1.
The table below demonstrates which behavior, old or new, is used for models based on the two APIs.
API |
IR v10 |
IR v11 |
ONNX file |
Model created in code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Inference Engine / nGraph APIs |
Old |
Old |
Old |
Old |
API 2.0 |
Old |
New |
New |
New |
Check these transition guides to understand how to migrate Inference Engine-based applications to API 2.0: